How to Feel Full Longer: Top Foods That Promote Satiety
We’ve partnered with Vitality Nutrition‘s Registered Dietitian Courtney Berg to share her best tips to help you improve your overall diet and maintain a healthy lifestyle. Click here to meet Courtney.
A common question I hear as a Registered Dietitian is, “Why do I always feel hungry—and how can I stay full longer to avoid constant snacking?”
If you find yourself constantly reaching for snacks or struggling to stay satisfied between meals, you’re not alone. The key to lasting fullness isn’t necessarily eating more—it’s eating with intention! By focusing on key strategies, you can better manage appetite and cravings, increase satisfaction, boost energy levels, and feel more in control of your eating habits.
Satiety is the feeling of fullness after eating that helps prevent hunger and reduces the urge to snack between meals. It is influenced by the nutrients in food as well as complex psychological, environmental, and social factors. In this article, we’ll focus on how specific foods impact satiety and appetite regulation!
1. Protein-Packed Foods
Protein is often considered the most satiating macronutrient as it regulates appetite by influencing hunger hormones. It decreases ghrelin (the hunger hormone) and increases satiety hormones such as peptide YY (PYY), glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1), and cholecystokinin (CCK), which slow gastric emptying and enhance feelings of fullness (1). Add a source of protein to your meals to increase satiety and feel full for longer!
High-Protein Sources for Satiety:
- Lean meats: Chicken, turkey, fish, seafood, lean cuts of beef or pork
- Eggs
- Dairy foods: Greek yogurt, cottage cheese, milk, cheese
- Plant-based proteins: Tofu, tempeh, lentils, beans (also a source of fibre!)
2. High-Fiber Foods
Dietary fiber decreases hunger and prolongs satiety by slowing digestion, stabilizing blood sugar, stimulating the release of satiety hormones (e.g., CCK, PYY, GLP-1), and promoting the production of short-chain fatty acids that further enhance satiety (2). Some of the best fiber-rich foods include:
High-Fiber Foods for Satiety:
- Vegetables: Broccoli, cauliflower, carrots, artichokes, beets, potatoes, bell peppers, and others
- Fruits: Apples, berries, pears, oranges, kiwis, and others
- Legumes: Beans, lentils, bean or lentil pasta (which also provide protein!)
- Nuts & Seeds: Chia seeds, ground flax, almonds, pumpkin seeds, walnuts
- Whole Grains: Quinoa, oats, barley, whole-grain breads
How to Incorporate More Fiber:
- Chia seeds: Sprinkle on yogurt bowls, stir into overnight oats, or make chia pudding.
- Oats: Prepare oatmeal bakes, overnight oats, or homemade oatmeal energy bites.
- Beans: Add canned black beans to taco salads, chili, or soups.
- Avocados: Use for toast, guacamole, or in smoothies.
- Raspberries: Add to yogurt bowls, oats, or smoothies.
3. Add in Some Healthy Fat
Healthy fats slow digestion and trigger satiety hormones like CCK, helping you achieve lasting fullness (3). Fats also provide essential nutrients and stabilize blood sugar to delay the onset of hunger while sustaining energy!
Healthy Fat Sources:
- Avocados (rich in heart-healthy monounsaturated fats and fiber)
- Nuts & Seeds (contain fat as well as protein and fibre)
- Olive Oil (a source of heart-healthy monounsaturated fats)
- Cheese or Full Fat Yogurt (contains fat as well as protein and micronutrients like calcium)
- Fatty Fish (salmon, sardines, and mackerel offer omega-3 fats and protein)
4. Voluminous Foods
“Volume foods” provide an increased sense of fullness due to their physical bulk while being relatively low in calories. These foods stimulate stretch receptors in the stomach and send signals to the brain that you’re full. Their fiber content also slows gastric emptying and digestion, prolonging satiety (4).
Best High-Volume Foods:
- Non-starchy vegetables: Lettuce, cucumber, zucchini, spinach, tomatoes, peppers, broccoli, cauliflower, others.
- Fruits: Berries, oranges, apples, kiwis, pears, others.
- Liquids like soups, smoothies, and consuming water which contain liquid, fiber, and/or volume to promote fullness.
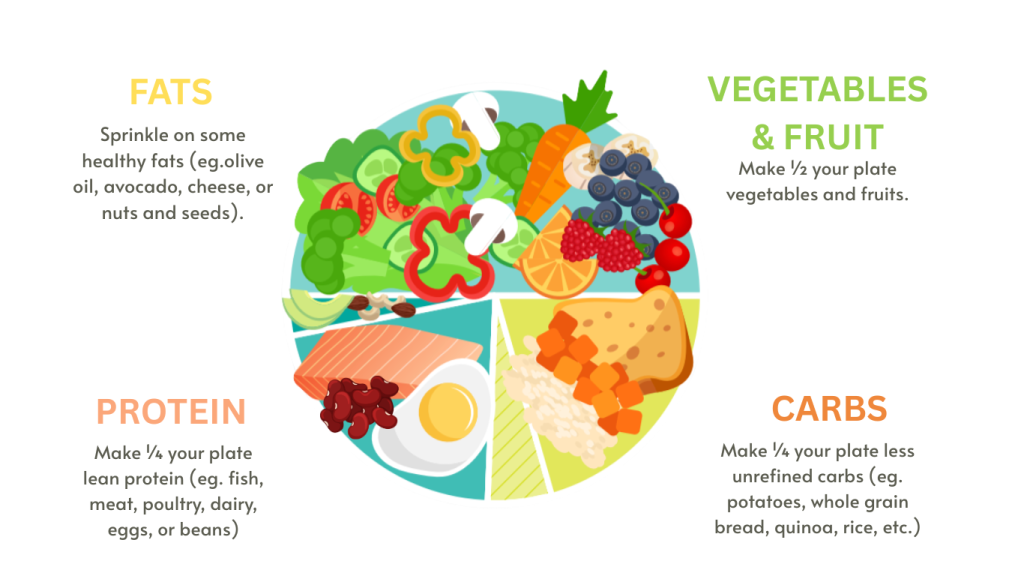
Dietitian Tip: Aim to make half your plate voluminous foods like vegetables and fruits!
5. Prepare Meals You Genuinely Enjoy
While physical fullness is crucial, appetite regulation extends beyond nutrients—psychological satisfaction plays a role in reducing cravings and promoting overall satiety!
Tips to Make Meals More Enjoyable:
- Reflect on cravings: Are you craving something crunchy, fresh, hearty, warm, sweet, or savory? Create a nutritious meal to match your preference!
- Experiment with flavors: Use seasonings, herbs, marinades, spices, dips, and sauces to enhance meals.
- Prioritize foods you love: Include favorite ingredients balanced with protein, fiber, and healthy fats (e.g., add crunchy taco chips to a taco salad with ground beef, black beans, veggies, guacamole, and cheese).
- Use mindful plating: Serve meals in an appealing way to increase enjoyment and satisfaction.
- Honor cravings in a balanced way: If you’re craving something that is less nutritious, try incorporating it in moderation rather than restricting it completely.
Summary of Strategies for Feeling Full Longer
- Prioritize protein at every meal to help regulate hunger hormones and slow digestion.
- Select high-fiber foods to slow gastric emptying and promote fullness.
- Don’t fear healthy fats—they contribute to satiety and provide essential nutrients!
- Choose high-volume foods such as vegetables, fruits, and liquids to increase stomach distention while managing caloric intake.
- Prioritize mental satisfaction by crafting meals you genuinely enjoy.
By focusing on these strategic foods and habits, you can better manage your appetite, avoid unnecessary snacking, and support your overall health. If you’re unsure where to start, consider working with a Registered Dietitian to tailor your nutrition plan to your unique preferences and goals!
References
- Beglinger, C., & Degen, L. (2007). “Gastrointestinal Satiety Signals in Humans – Physiologic Roles for GLP-1 and CCK.” Gastroenterology, 132(6), 2091-2106. Available here.
- Brennan, I. M., Luscombe-Marsh, N. D., Seimon, R. V., Otto, B., Horowitz, M., & Feinle-Bisset, C. (2022). “Effects of Macronutrients on Gut Hormone Release and Appetite Control: A Review.” PubMed. Available here.
- Ballinger, A., & Clark, M. (1994). “Role of Cholecystokinin in Satiation: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.” British Journal of Nutrition, 71(1), 3-21. Available here.
- Blundell, J. E., Finlayson, G., Gibbons, C., Caudwell, P., & Hopkins, M. (2018). “The Hunger Obesity Paradox: Obesity as a Condition of Hyperphagia.” Physiology & Behavior, 192, 101-107. Available here.
Meet Courtney Berg, RD, B.Sc. Nutrition
About Courtney | Courtney Berg is a Registered Dietitian and completed her Bachelor’s Degree in Nutrition from the University of Saskatchewan in 2016. Her approach to nutrition continues to evolve as she learns and grows with her clients at Vitality Nutrition. However, a holistic approach remains the base of her philosophy with an emphasis on understanding how nutrition as well as sleep, mindset, exercise, and the environment work together to influence whole body health.
About Vitality Nutrition | Vitality Nutrition is a collective of Registered Dietitians and Nutritionists supporting clients in Saskatchewan and across Canada! We incorporate a unique and meaningful approach to food, fitness, and performance that empowers clients to build life-long habits and see lasting results.
